What Hereditary Factors Were Described by Mendel
He also observed that factors can be dominant or recessive. Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 an Austrian monk is considered the father of genetics.
The hereditary factors from Mendels experiments are actually single chromosomes.

. Mendels factors genes reside on chromosomes DNA was the heredity material. By crossing this YYRR plant to a pure breeding plant with green wrinkled peas annotated yyrr plants heterozygous for each factor YyRr would arise the F1 generation. Genes Reside on Chromosomes 1879-1892 Flemming Strasburger Waldeyer van Beneden and Weismann developed the concept of chromosomes Flemming 1882.
The big A shows the dominant factor and small a shows the recessive factor. Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment Genes Reside on Chromosomes Eduard Strasburger 1876. But sperm contains little cytoplasm.
Up to 24 cash back What did Gregor Mendel conclude about heredity. See full answer below. Law of Segregation 3.
Genes can be called the units of inheritance. Mendels factors were later called Genes and associated to DNA. What does Mendels first law mean.
Mendels model suggests that these two gametes transfer equal hereditary material in the zygote. By picking a species with a handful of visible characteristics that occur in two easily identifiable forms Mendel was able to pinpoint what he called factors These factors determine traits like a peas shape or color for instance and are passed down from parents to offspring. For example the gene for flower color in pea plants exists in two forms one for purple and the other for white.
What is Mendels factor. Mendels three principles of Inheritance are. Mendel the first person to trace the characteristics of successive generations of a living thing was not a world-renowned scientist of his day.
Mendel theorized that genes could be formed up by three possible combinations of heredity units that are said to be factors. Mendelian factors are simply genes. If the alleles are the same it is called a Homozygous.
Chromosome Strands of human chromosomes. Law of Dominance 2. In the mid-1850s Mendel became interested in hybridization and began breeding garden peas.
The focus of genetics research then shifted to understanding what really happens in the transmission of hereditary traits from parents to children. Mendel found that there are alternative forms of factorsnow called genes that account for variations in inherited characteristics. It seemed that Mendels ideas were of general validity.
By the 1890s the invention of better microscopes allowed biologists to discover the basic facts of cell division and sexual reproduction. Mendel also developed the law of dominance in which one allele exerts greater influence than the other on the same inherited character. He performed monohybrid and dihybrid crosses and gave three principles of inheritance.
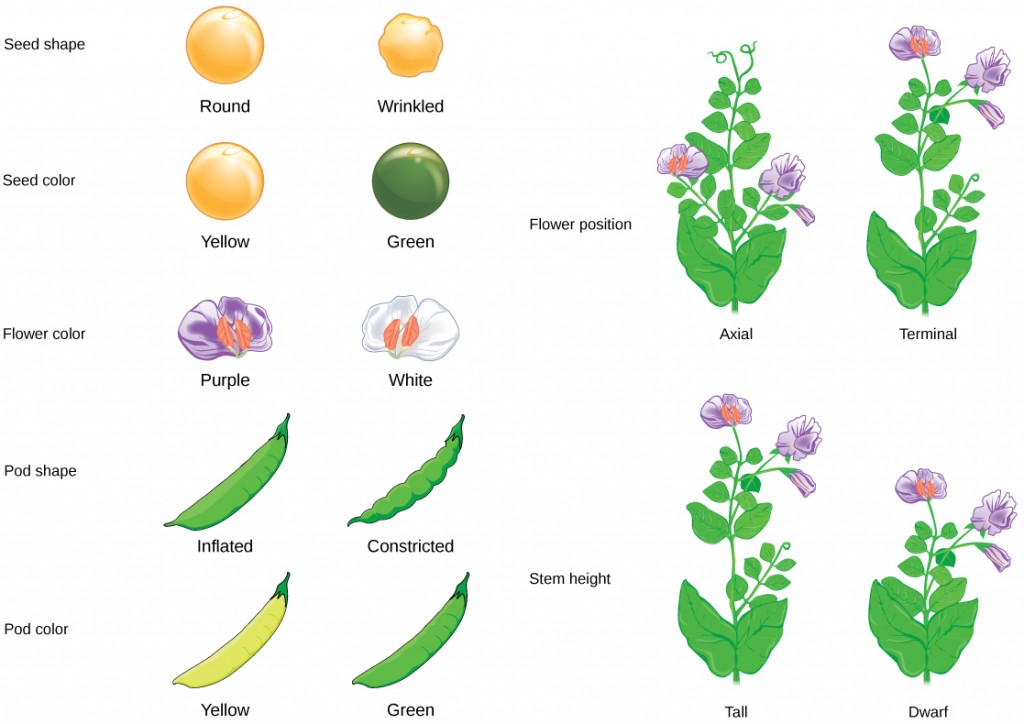
Mendel experimented on a pea plant and considered 7 main contrasting traits in the plants. Mendel studied the inheritance of various traits in pea plants. The short monograph Experiments with Plant Hybrids in which Mendel described how traits were inherited has become one of the most enduring and influential publications in the history of science.
Mendel developed the concept of dominance from his experiments with plants based on the supposition that each plant carried two trait units one of which dominated the other. Mendel while performing the experiment on inheritance of traits characteristics used the term factors for the units which code for these traits. Many biologists noted that the inheritance of genes closely paralleled the inheritance of chromosome s during nuclear divisions called meiosis that occur in the cell divisions just prior to gamete formation.
Mendel In the latter part of 19 th century. Mendelian Heredity return to Themes list. The genes were called Mendelian factors.
Thomas in Brno Moravia now the Czech Republic. Naming the Mendelian Laws Correns 1900 o Referred to segregation and assortment Morgan 1916 o First to use the terms. After analysing his results Mendel concluded that 2 factors control each inherited trait.
A number of hypotheses were suggested to explain heredity but Gregor Mendel a. For the pure breeding plant with yellow and round peas Mendel would have annotated the two dominant factors underlying these traits as YY and RR respectively. Mendel described seven different heredity factors or alleles by crossing pea plants tracking the inheritance of the traits they code for.
One such trait is whether the pea is smooth or wrinkled. Gregor Mendel developed some basic principles of heredity by. Below is a Punnett square showing a cross between two parents.
He then conceived the idea of heredity units which he called hereditary factors. In one experiment he observed 423 smooth and 133 wrinkled peas. In human body cells there are.
Like white flowers A plant with two different factors would show the dominant factor but still. Mendel predicted a ratio of 3 smooth peas for every 1 wrinkled pea. While experimenting Mendel found that certain factors were always being transferred down to the offspring in a stable way.
Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 was a monk of the Augustinian monastery of St. The beginning plants were homozygous AA or aa F1 generation was Aa and F2 generation was AA aa or Aa. Mendels Law of Inheritance or Mendelian genetics It is a set of primary tenets that underlie much of genetics by G.
Thus hereditary material is present within nuclei of gametes. Later these factors were given the term genes. The hereditary factors from Mendels experiments are actually genes located on chromosomes.
Mendels factors genes reside on chromosomes DNA was the heredity material. Become a member and. At the time of Mendel DNA had not yet been associated with inheritance.
Chromosomes can be found within alleles accounting for different phenotypic traits. The forms of a Mendelian factor a Gene are known as Alleles. Some traits could only be observed if a plant had two of the same factors.
Those factors are now called genes ie. The principles of dominance segregation and independent assortment were first described by. See answer 1 Best Answer Copy The first person to put heredity to the test was Gregor Mendel who systematically tracked dominant and recessive traits in his famous pea plants.
The pea plants have two alleles constituting its Genotype. Mendels work was rediscovered his factors were renamed genes and his ideas. Pairing of Chromosomes and Genes Diploid individuals have two copies of each pair of homologous chromosomes.

Mendel S Laws Of Inheritance Vs Human Evolution Inheritance Gregor Mendel Genetics

No comments for "What Hereditary Factors Were Described by Mendel"
Post a Comment